Foundation Repair Cost Calculator
Repair Options & Costs
Financial Impact Assessment
Repair Cost Estimate
$0.00
Mortgage Impact
Resale Value Impact
Financial Summary
Thinking about snapping up a property that shows signs of a shaky base? It’s a tempting bargain, but a faulty foundation can turn a dream home into a financial nightmare. This guide breaks down what you need to know-risk factors, inspection tricks, repair options, and how the issue affects your mortgage and resale value-so you can decide if the deal is worth the risk.
What Exactly Is a House Foundation?
House foundation is the structural element that transfers a building’s load to the earth below.It typically consists of footings, slab, crawl‑space walls, or a full basement, all designed to keep the home level and stable over time. When a foundation fails, cracks appear in walls, doors stick, and the entire structure can settle unevenly.
Why Foundations Fail: Common Causes
- Expansive or shrinking soil conditionslike clay that swells with moisture or dries out and contracts.
- Poor drainage leading to water pooling around footings
- Improper foundation designthat doesn’t account for load distribution or local frost depth.
- Heavy loads from new additions or equipment placed too close to the structure
- Tree roots excavating soil beneath the slab
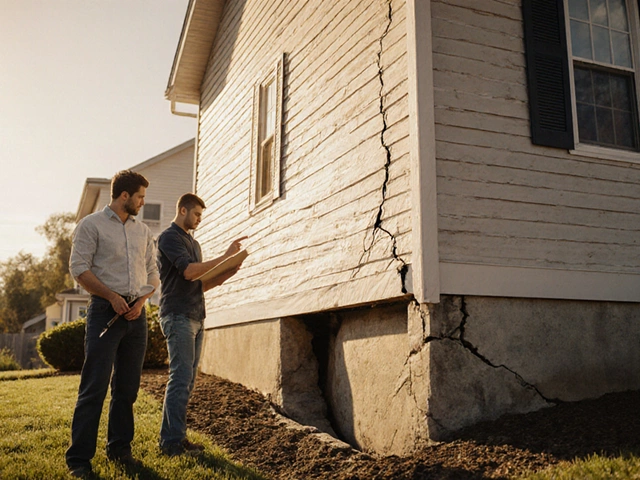
Assessing the Severity: How a Home Inspection Helps
A qualified home inspectorexamines visible signs like cracks, uneven floors, and moisture patterns. They’ll flag potential red flags, but remember they aren’t structural engineers. For a definitive answer, hire a structural engineerwho can perform load calculations, soil testing, and recommend repair strategies.
Repair Options and Typical Costs (2025 Canada)
| Method | When It’s Used | Typical Cost Range (CAD) |
|---|---|---|
| Helical piers | Soil settlement, moderate cracks | $8,000 - $15,000 |
| Push piers (concrete pilings) | Severe settlement, poor soil bearing | $12,000 - $25,000 |
| Basement wall anchors | d>Bow‑ing walls, lateral pressure | $5,000 - $12,000 |
| Slabjacking (mudjacking) | Minor settlement, cracks in slabs | $3,000 - $7,000 |
| Full foundation replacement | Catastrophic failure, extensive damage | $50,000 - $150,000+ |
These numbers vary by province, local labor rates, and access constraints. Halifax, for example, sees higher costs on piers because of the coastal climate’s freeze‑thaw cycles.
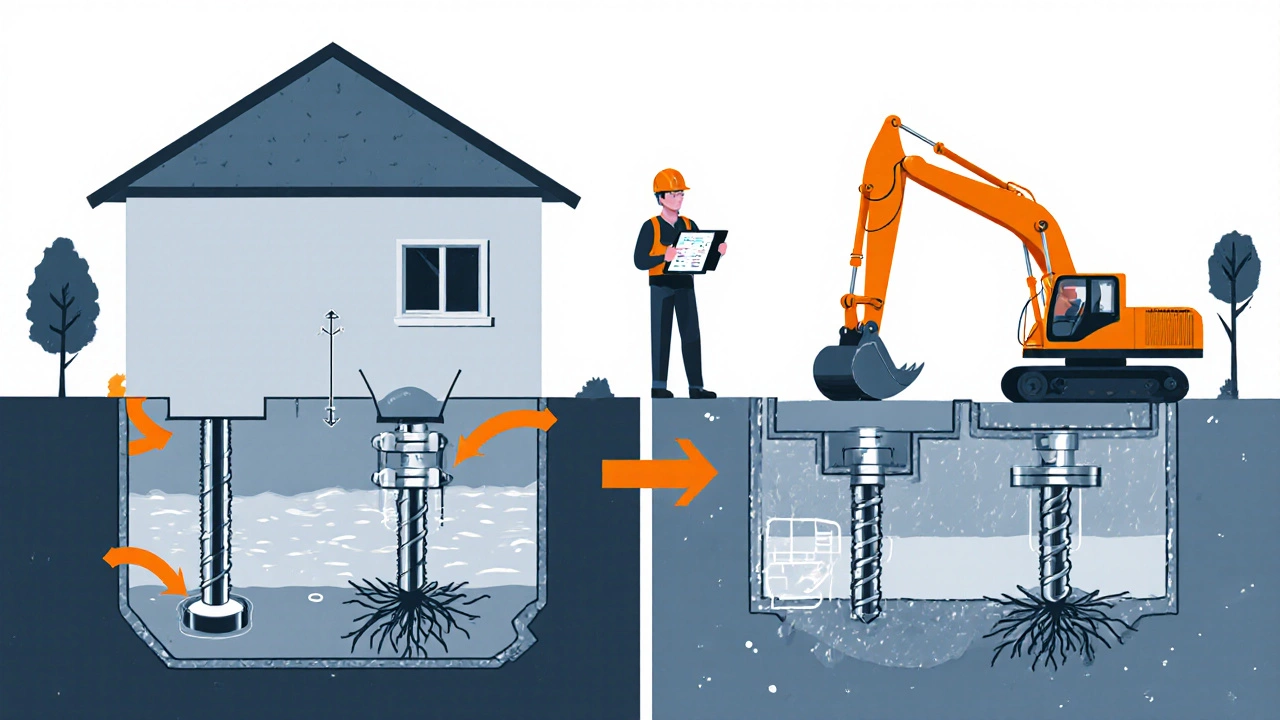
Financing the Fix: Mortgage and Insurance Implications
Most mortgage lendersrequire a clear title and no major structural issues before approving a loan. If a foundation problem is found, the lender may:
- Reduce the loan‑to‑value (LTV) ratio until repairs are completed.
- Demand an appraisal after the repair.
- Require a higher interest rate to offset perceived risk.
Homeowners’ insurancetypically excludes coverage for foundation repairs caused by soil movement. So you’ll be paying out‑of‑pocket unless the defect stems from a contractor’s negligence.
Resale Value: How Foundation Issues Affect Future Sales
Buyers are wary of unseen structural problems. A property with a disclosed foundation repair can still sell, but you’ll likely see a price dip of 5‑15 % compared to similar homes in the same neighbourhood. The key is transparency: provide the engineer’s report, detailed repair invoices, and warranties. Those documents can reassure buyers and keep the loss to a minimum.
Decision Checklist: Should You Buy?
- Get a professional inspection. A home inspector’s report is your first filter.
- Hire a structural engineer for a detailed assessment and a repair estimate.
- Compare repair cost against the home’s market value and your budget.
- Talk to your mortgage lender about loan adjustments or required escrow funds for repairs.
- Check local building codesto ensure the proposed fix meets regulations. and any permit fees.
- Factor in future resale impact-calculate a realistic post‑repair selling price.
- If you’re still on the fence, consider negotiating a price reduction equal to the repair estimate.
Following this checklist helps you avoid hidden costs and turn a potential money‑sink into a savvy investment.

Common Pitfalls and How to Dodge Them
- Assuming all cracks are cosmetic. Horizontal cracks in block walls often signal serious pressure.
- Skipping the structural engineer because you think the inspector’s report is enough.
- Agreeing to a “quick fix” like epoxy injection without addressing the underlying soil issue.
- Underestimating the time needed for repairs; many projects take 4‑8 weeks, affecting moving plans.
- Failing to get a post‑repair inspection-without it, you might still face undisclosed problems later.
Real‑World Example: A Halifax Bungalow Turned Around
In March 2024, a buyer fell in love with a 1990s bungalow listed for $420,000. The inspector noted 1‑inch cracks in the living‑room wall and a sloping basement floor. A structural engineer recommended helical piers costing $13,500. The buyer negotiated a $12,000 price drop, closed the deal, and completed repairs over summer. Six months later, the home sold for $465,000, yielding a net profit after repair costs. The lesson? Accurate estimates and strategic negotiation can turn a seeming red flag into a profitable flip.
Quick Reference Cheat Sheet
| Item | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Foundation repair cost (average) | $8,000‑$25,000 |
| LTV reduction for major issues | 10‑20 % |
| Resale price penalty | 5‑15 % |
| Average permit fee (Halifax) | $500‑$1,200 |
Bottom Line: Is It Okay to Buy?
If you do your homework-professional inspection, engineered repair plan, realistic budgeting, and mortgage clearance-buying a house with foundation problems can be a smart move. The crucial part is knowing exactly what you’re getting into and having the money set aside for a proper fix. Skipping any step can leave you stuck with costly surprises down the line.
What signs indicate a serious foundation problem?
Look for wide cracks (over ½ inch) in walls, doors that won’t close, uneven floors, and water pooling in the basement. Horizontal cracks in block walls or a sloping foundation are especially concerning.
Can I get a mortgage if the house needs foundation repair?
Most lenders will still finance the purchase, but they may lower the loan‑to‑value ratio, require a higher interest rate, or hold funds in escrow until repairs are completed and verified.
How long do foundation repairs typically take?
Simple slabjacking can be done in a day or two, while installing piers or replacing a basement wall may take 4‑8 weeks, depending on weather and access.
Will a repaired foundation affect my home insurance?
Insurance usually doesn’t cover foundation repairs, but after a professional fix, you can provide the receipt to the insurer, which may lower your risk rating.
Is it better to negotiate the price down or ask the seller to fix the foundation?
Both work, but a price reduction gives you control over the repair schedule and choice of contractor. Ensure the reduction covers at least 100 % of the engineer’s estimate.






